The British pound rebounded strongly to around 1.3465 against the US dollar during the European trading session on Monday after a weak open around 1.3390. GBP/USD bounces back as the US dollar corrects sharply, after a criminal investigation was opened into Federal Reserve Chairman Jerome Powell over mismanagement of funds in the rebuilding headquarters in Washington.
At the time of writing, the US Dollar Index (DXY), which tracks the value of the dollar against six major currencies, is trading 0.3% lower near 98.80. The DXY index rebounded after revisiting the monthly high near 99.25.
Over the weekend, the US Department of Justice sent a subpoena to the Federal Reserve for Jerome Powell, which is directing an investigation into his statements during Senate testimony in June 2025 and an examination of his spending records.
In response, the Fed’s Powell also stated that “the new threat is not about his testimony or the renewal project but about the pretext.” Powell added that the threat of criminal charges is “the result of the Fed setting interest rates based on its assessment of the public interest rather than the president’s preferences.”
Market experts believe that the criminal charges against Federal Reserve Chairman Powell escalated his dispute with US President Donald Trump, who has criticized him several times since his return to the White House for not lowering interest rates. This could lead to a serious decline in the Fed’s independence, which is an unfavorable situation for the US dollar.
US dollar price today
The table below shows the percentage change in the US Dollar (USD) against the major currencies listed today. The US dollar was the weakest against the Swiss franc.
| US dollars | euro | GBP | JPY | Canadian | Australian dollar | New Zealand dollar | Swiss franc | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| US dollars | -0.47% | -0.39% | -0.03% | -0.24% | -0.27% | -0.39% | -0.56% | |
| euro | 0.47% | 0.08% | 0.44% | 0.22% | 0.20% | 0.08% | -0.09% | |
| GBP | 0.39% | -0.08% | 0.34% | 0.14% | 0.12% | -0.00% | -0.17% | |
| JPY | 0.03% | -0.44% | -0.34% | -0.21% | -0.24% | -0.36% | -0.52% | |
| Canadian | 0.24% | -0.22% | -0.14% | 0.21% | -0.02% | -0.14% | -0.31% | |
| Australian dollar | 0.27% | -0.20% | -0.12% | 0.24% | 0.02% | -0.12% | -0.30% | |
| New Zealand dollar | 0.39% | -0.08% | 0.00% | 0.36% | 0.14% | 0.12% | -0.17% | |
| Swiss franc | 0.56% | 0.09% | 0.17% | 0.52% | 0.31% | 0.30% | 0.17% |
The heat map shows the percentage changes in major currencies versus each other. The base currency is chosen from the left column, while the counter currency is chosen from the top row. For example, if you select USD from the left column and move along the horizontal line to the Japanese Yen, the percentage change displayed in the box will represent USD (base)/JPY (quote).
Daily Summary Market Movers: Fed’s Bostic warns of inflation risks
- Looking to the UK, the pound is expected to be driven by UK employment data for the three months ending November this week, which will be released on Tuesday. Investors will pay close attention to UK labor market data for new signals on the Bank of England’s (BoE) monetary policy outlook.
- In 2025, UK labor market concerns will remain high as companies avoid aggressive hiring to offset the impact of higher employer contributions to social security schemes.
- Meanwhile, the monthly survey conducted by the Trade and Employment Commission (REC) and accountants KPMG earlier today showed that labor demand remained weak while wage growth accelerated in December.
- In the United States, the December nonfarm payrolls report on Friday showed that the unemployment rate fell sharply to 4.4% from 4.6% in November. However, employment was lower at 50K versus estimates of 60K and previous reading of 56K.
- Going forward, the next major catalyst for the US dollar will be the release of Consumer Price Index (CPI) data on Tuesday. Investors will closely monitor US inflation data for new signals about interest rate expectations.
- In 2025, the Fed made three 25 basis point interest rate cuts in an attempt to contain labor market problems, even as inflation remains well above the 2% target for an extended period.
- On Friday, Atlanta Fed President Rafael Bostic said in an interview with radio station WLRN that inflation is “too high” and that the Fed needs to “get it under control.”
Technical Analysis: GBP/USD attracts bids below the 20-day EMA
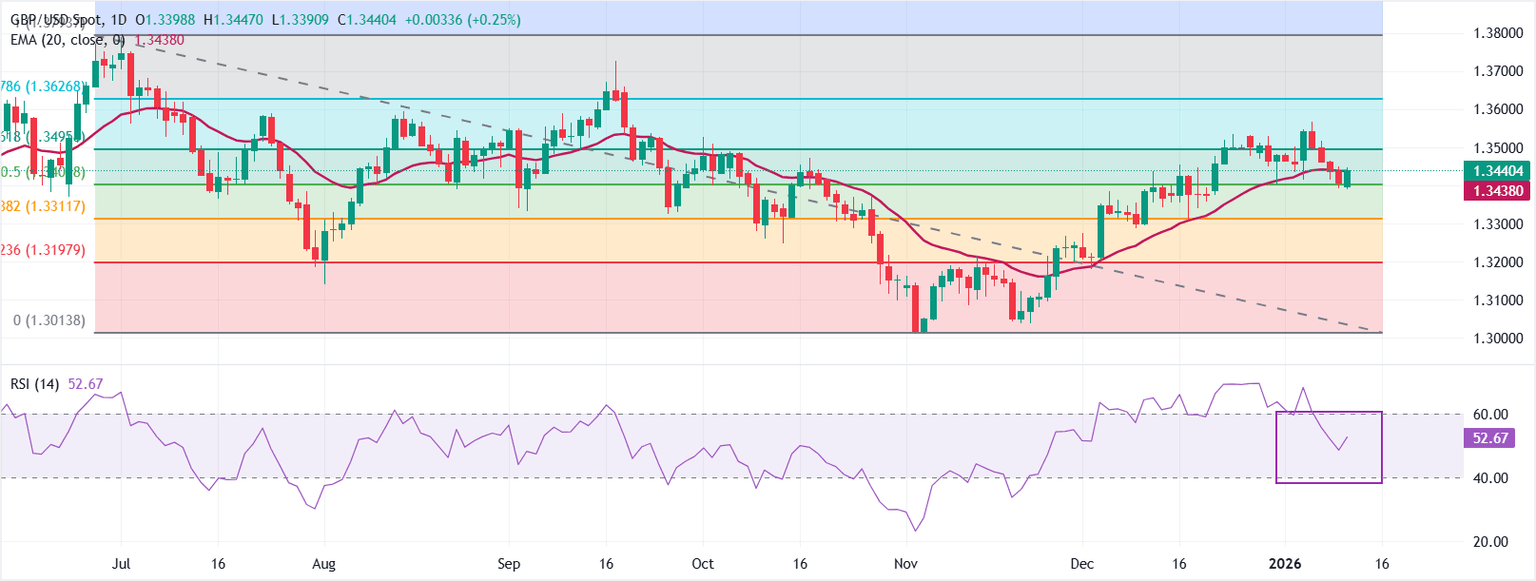
GBP/USD is trading at around 1.3465 at the time of writing. The 20-day Exponential Moving Average (EMA) is rising and located at 1.3438, with the price holding just above it, supporting the uptrend.
The 14-day Relative Strength Index (RSI) has turned at 53 (neutral) to the upside, confirming steady momentum.
Measured from the high of 1.3794 to the low of 1.3014, the 61.8% retracement at 1.3496 acts as immediate resistance. A decisive break above this level will indicate that the downtrend is losing strength and could open further upside towards the September 17 high at 1.3726.
Conversely, failure to cross 1.3496 would keep the pair in check, with a return drift towards the 50% retracement level at 1.3404 dampening momentum and keeping the bounce within a narrow range.
(The technical analysis for this story was written with the help of an artificial intelligence tool.)
Economic indicator
Consumer Price Index (annual)
Inflationary or deflationary trends are measured by periodically collecting the prices of a basket of representative goods and services and presenting the data as the Consumer Price Index (CPI). Consumer Price Index (CPI) data is compiled on a monthly basis and released by US Department of Labor Statistics. The annual reading compares commodity prices in the reference month with the same month of the previous year. The Consumer Price Index is a key indicator for measuring inflation and changes in purchasing trends. In general, a high reading is considered bullish for the US Dollar (USD), while a low reading is considered bearish.
Read more.
Next release:
Tuesday 13 January 2026 at 1:30
repetition:
monthly
consensus:
2.7%
former:
2.7%
source:
US Bureau of Labor Statistics
The US Federal Reserve has a dual mandate of maintaining price stability and maximum employment. According to this mandate, inflation should be around 2% year-on-year, and it has become the weakest pillar of the central bank’s guidance since the world suffered from the pandemic, which extends to the present day. Price pressures continue to rise amid supply chain issues and bottlenecks, with the Consumer Price Index remaining at multi-decade highs. The Fed has already taken measures to tame inflation and is expected to maintain a strong stance for the foreseeable future.


